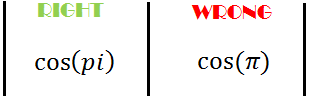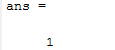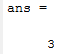These are a few basic tools you will need to know if you are just starting learning Matlab.
Scalar functions in Matlab
Before fully diving into trigonometric functions, it is necessary to state that Matlab takes as input radians while working with trigonometric function meaning and uses the symbol pi for π
Trigonometric sine
Matlab code
sin(pi)
Trigonometric cosine
Matlab code
cos(pi)
Trigonometric tangent
Matlab code
tan(3*pi/2)
Trigonometric inverse sine (arcsine)
Matlab code
asin(1)
Trigonometric inverse cosine (arccos)
Matlab code
acos(0.5)
Trigonometric inverse tangent (arctan)
Matlab code
atan(3/2)
e Matlab (exponential)
Matlab code
exp(x)
Natural logarithm
Matlab code
log(5/2)
Absolute value
Matlab code
abs(a*x+b)
Square root
Matlab code
sqrt(a*b)
Remainder after division
This function helps you find the remainder after a division. We will use as an example the remainder of the division of 5 by 2, which is one.
Matlab code
rem(5,2)
which returns
Round towards nearest integer
This function will allow you to round values towards the nearest integer if you are not interested in working with decimal numbers. It is most useful while you want to round the result of an operation.
Matlab code
round(2.9)
Which returns
Round towards negative infinity
floor(x) rounds the elements of x to the nearest integers towards minus infinity.
Round towards positive infinity
As opposed to the floor function, ceil(x) rounds the elements of x to the nearest integers towards infinity.